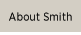The Ballet Nacional de Cuba is one of the most prestigious dance companies in the world, founded by Alicia Alonso with the support of Fidel Castro’s government, along with a network of ballet schools that to this day produces some of the most acclaimed dancers in the world. Among the important works in the company’s repertoire is Swan Lake.
/ Published January 15, 2014
Cuba has long had a vibrant and even dazzling dance culture. But surprisingly, the island nation is also recognized internationally as an important center for training in and appreciation of ballet—a highly stylized form of movement with conventions going back to the imperial courts of France and Russia.
Assistant Professor of Dance Lester Tomé, who launched his professional life first as a journalist covering the arts while an undergraduate at the University of Havana, has been studying the contradictions this presents—particularly how the Caribbean island nation with a staunch socialist ideology came to embrace what many view as an elitist art form which, he says, started as a “spectacle to illustrate the wealth of monarchs.”
“On one hand,” Tomé notes, “the initial reactions of European and American critics looking at Cuban dancers was one of surprise and skepticism: ‘How is it possible for Caribbean people to dance ballet? What do they know about it? Do they have the cultural knowledge and the right types of bodies to perform ballet?’” Those kinds of questions go back to the 1940s when the Cuban ballerina Alicia Alonso established herself as one of the premier interpreters of Giselle, a famous role in the ballet canon.

Lester Tomé
The contradiction became especially apparent after the Cuban Revolution in 1959, says Tomé. “Some Cuban and Latin American intellectuals questioned the appropriateness of cultivating ballet in the region. For them, the genre symbolized European aristocratic culture. They perceived its adoption as perpetuating Eurocentric attitudes and cultural colonialism in Latin America.”
Tomé, who teaches dance history and Latin American studies and who writes about the intersection of dance and culture, recently received a grant from the National Endowment for the Humanities to examine Cuba as a case study in what he sees as the globalization of ballet. The phenomenon extends not only to the fact that dancers all over the world study classical dance, but also to the adaptation and blending of ballet with local cultures in various Asian and Latin American locations. In the case of Cuban culture, such syncretic practices are not unusual—as in Santería or the hybridization of ballet and Afro-Caribbean dance traditions like rumba.
Although Tomé has a few performing credits to his name—and has taught dance theory and offers a salsa class at Smith (which alternates meetings between the classroom and the studio)—he is not a practitioner. “I am a scholar, not a dancer,” he says. “Sometimes I have crossed the boundary between the two, but my training and background is as a journalist, critic and researcher.”
As an academic with roots in journalism, Tomé does much of his research through interviews. He grew up in the Villa Clara region of Cuba and moved to Havana to study journalism in the early 1990s, a tumultuous time marked by shortages and economic crisis as Cuba lost its trade partners with the fall of communism in Europe. He secured an internship with CMBF—Radio Musical Nacional, a classical radio station, where he reported on dance for four years. After graduation he moved to Chile and spent the next six years writing about dance for El Mercurio, one of the oldest newspapers in Latin America.
Turning to academia, Tomé went to Philadelphia to earn his doctorate at Temple University, where he developed his interest in studying the work of Alicia Alonso— a figure who embodied many of the contradictions that fascinate him. “There was the paradox of a world-class ballerina coming from Cuba,” he says. She was dancing with the American Ballet Theatre in New York in the 1940s, at a time when American ballet dancers were disregarded as not being on a par with the Russian, French and British stars who dominated international ballet. “She helped defeat that stereotype,” he says, which was all the more remarkable because she had endured several eye operations that left her legally blind. Alonso was the first American dancer of that generation to achieve international recognition in classical productions such as Giselle and Swan Lake, at that point regarded as the exclusive province of European ballerinas. In the 1940s and ’50s, she achieved great success not only in the United States, Cuba and Latin America, but also in Britain, France and the Soviet Union.
Then, after the Cuban Revolution, Alonso abandoned a glamorous international career to return to her homeland permanently. With the support of Fidel Castro’s government, she founded the Ballet Nacional de Cuba and a network of ballet schools that to this day produces some of the most acclaimed dancers in the world. These include figures like the Afro-Cuban dancer Carlos Acosta, a star of the Royal Ballet in London since 1998.
Tomé says his scholarship is in part a response to the fact that most ballet historians ignore the many ways in which the dance form has evolved into a multi- and cross-cultural phenomenon flourishing beyond Europe and North America. “The face of ballet has changed over the past decades, but the way in which historians write about ballet has not changed,” he says. “The notion that ballet is an art for European and Euro-American bodies is not current anymore. Not only is ballet practiced across the globe, but ensembles in cities like New York and London have grown truly international in their composition—with Asians and Latin Americans dancing with North Americans and Russians.”
Ballet underwent a transformation in Cuba after the revolution. “Dancers consciously decided to promote a new image of ballet as an art of the people that was aligned with the proletariat ideology of the revolution,” says Tomé. “They performed on military bases for soldiers, in the countryside for farmers and in factories for workers....They brought ballet to the people, and thus it became a popular art with a broad audience.”

Tomé sees the casting of white and black dancers as “a metaphor for the integration of European and African culture in Cuba.” But it is also political. “Eliminating racism was one of the goals of the revolution. The Ballet Nacional embraced Afro-Cubans, who had previously been excluded from ballet.”
Cuba has seen a sustained effort to cast ballet as a national art form by creating works that incorporate Afro-Cuban culture. “The island’s poems, novels and music as well as events from Cuban history have been incorporated into new ballets,” says Tomé. “I argue that there is a tension between cosmopolitanism and nationalism in Cuban culture and that ballet makes this evident.”
The search for a national voice has been present even in the performance of a foreign repertoire. “Alonso claimed to bring a Cuban sensibility, a Cuban aesthetic to performances of works like Coppélia or Les Sylphides even if she was doing exactly the same choreography that a Russian ballerina or a French ballerina was doing. In her view, certain forms of musicality and bodily expressivity distinguish Cuban dancers.”
Therein lie some of the answers to the paradoxes that first captured Tomé’s imagination. “Ballet is flexible in that it can be readapted, and it lends itself to new developments,” he explains. This is evident not only in Cuba. In the U.S. and Argentina, for instance, choreographers have experimented with fusions of ballet and, respectively, jazz and tango. “People manipulate this art to make it an expression of their own culture.”
Tomé’s NEH project is "Cuban Ballet, Cosmopolitan Dancers and Nationalist Gestures: A Study in Ballet and Globalization." By drawing attention to the prominence of ballet on the island, he wants to show that—even if Europeans may regard Cuba as a cultural “other”—this is a country very much in dialogue with its European heritage. “Cuba is known for rumba, mambo, salsa and other expressions of the Afro-Cuban dance culture, but also for ballet. Its culture is a hybrid of African and European heritages.”
One consistent thread running through Tomé’s professional pursuits—from his undergraduate days covering the arts in Havana as a journalist to his role now as a Smith professor currently on a yearlong research fellowship at Harvard’s David Rockefeller Center for Latin American Studies—is an abiding interest in the interplay between cultures. “In looking at the development of the Cuban ballet, I ask a basic question: If you take something outside its original context and you put it somewhere else, what are the transformations it goes through?”